News & Events
Industry News
-
Espicom: The Global Advanced Wound Care Market to 2015
-
15/04/2011
-
There are significant growth opportunities in the advanced wound care market as well as a pressing need for clinical evidence to show the effectiveness of the technologies says Espicom Business Intelligence. Here are some highlights of its latest market analysis and future projections.
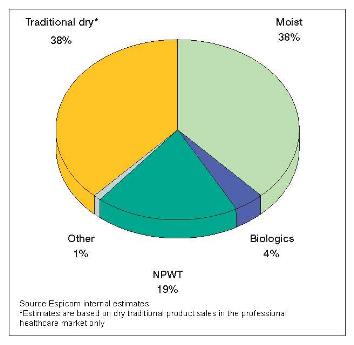
The advanced wound care market includes an array of competing technologies. Moist wound care dressings form the largest sector. These include hydrogels, hydrocolloids, alginates, foams and transparent films. More recently, these products have been combined with antimicrobial agents such as silver, iodine or honey to prevent and combat infection in wounds. In addition to aiding healing, the use of antimicrobial dressings can reduce the need for antibiotics and therefore concerns about antibiotic resistance.
The main device-based technology used in advanced wound care is negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), pioneered by Wake Forest University and Kinetic Concepts in the 1990s. This non-invasive treatment uses localised sub-atmospheric pressure to manage wounds by removing fluid and infectious materials, protecting the wound environment, promoting perfusion and a moist healing environment, and drawing together the wound edges. Other therapies in this sector are electrical stimulation and ultrasound to promote wound healing.
An emerging area of the advanced wound care market is the development of biologic products, which include collagen dressings, growth factors, skin substitutes and gene and stem cell therapy technologies to aid wound healing. Wound care biologics were originally developed to cover burn injuries in patients with insufficient sources of skin for grafting. Since then, skin substitutes have been developed and used to address the prevalent problem of chronic wounds associated with non-burn aetiologies.
1. Applications
The role of advanced wound care products is to treat more complex wounds, including chronic wounds, burns and complex surgical or trauma wounds. Chronic and complex wounds represent one of the biggest challenges to healthcare systems because they are difficult to heal and consequently expensive to treat.
Professional wound care market by product type, 2009
Diabetic ulcers. The number of elderly patients and people with diabetes is increasing and expected to continue to rise. This leads to a corresponding rise in the number of diabetic ulcers requiring treatment and a strong demand for advanced wound care products in the future, as well as more interest in the development of better products.
The International Diabetes Federation estimates that there were 285 million people with diabetes globally in 2009 and that the total number will exceed 435 million in 2030 if current rates of growth continue unchecked. Developed world studies have estimated that 15% of people with diabetes will ultimately have diabetic foot ulcers.
Pressure ulcers. On the basis of available data, new pressure ulcers are estimated to occur in 4 to 10% of patients admitted to acute hospitals in the UK. In the community, it is not known what proportion of people is affected by new pressure ulcers because reliable data are not available. However, a review by Kaltenthaler and colleagues in 2001 found the rates of pressure ulcers in the community in the UK vary between 4.4 and 6.8%.
To treat pressure ulcers, the UK's National Institute of Clinical Excellence recommends the use of advanced wound care dressings such as hydrocolloids, hydrogels and foams in preference to basic dressings such as gauze, paraffin gauze and simple dressing pads. Sometimes other treatments may be needed, including electrical stimulation and NPWT.
Venous stasis ulcers. These are the most common form of leg ulcers. It has been estimated that more than 600,000 people are treated for venous leg ulcers each year in the US. However, this number is likely to be an underestimation of the true prevalence of venous ulceration because many patients fail to seek medical care. Estimates range from 1 to 2% of populations studied.
2. Market Competitors
Currently, the advanced wound care market is dominated by Kinetic Concepts (KCI) and its NPWT products, as well as by Smith & Nephew, ConvaTec, Molnlycke Health Care, Systagenix Wound Management (previously Johnson & Johnson Wound Management) and Coloplast, all of which are predominately focused on moist wound care products.
With many companies not disclosing their advanced wound care sales, it is difficult to provide exact market share percentages for every company. However, Espicom believes KCI held 27% of the market in 2009, Smith & Nephew 16.5%, ConvaTec 10%, Molnlycke 9%, and both Systagenix and Coloplast 6%, and 25% was held by smaller and privately held companies.
3. Merges and Acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions play a critical role in the wound care industry. They have enabled the market leaders to expand their technology to address new sections of the market or provide them with access to new technologies so they are not left behind.
Transactions in 2010 included Healthpoint's purchase of two cell-based technologies from Intercytex and Mesoblast agreeing to acquire Angioblast. This provided it with new stem cell-based technology in development mainly for cardiac regeneration, but also for treating skin ulcers. These transactions provide Healthpoint and Mesoblast with new intellectual property and development pipelines in the promising area of biologics.
One company to have recently gained a presence in the advanced wound care market is Israeli pharmaceutical company, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries. Teva has shares in MediWound, which has developed the Debrase Gel Dressing, a bromelain-based enzymatic debriding agent. In June 2010, MediWound signed a memoranda of understanding with Polyheal, a company that has developed a microsphere-based technology for treating hard-to-heal wounds. Under the terms of the agreement, MediWound would gain an exclusive licence to manufacture and develop Polyheal's products, which Teva would exclusively commercialise.
4. Future Growth
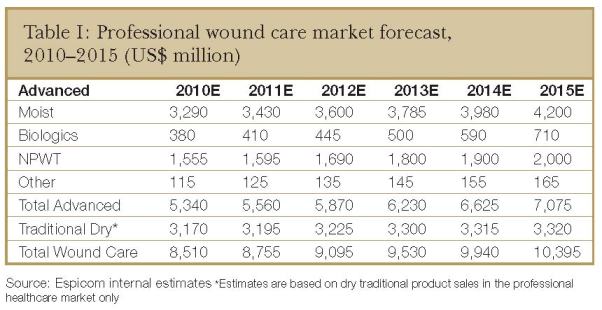
Given the fragmented nature of the wound care market and the number of private companies operating in this area, it can be challenging to quantify the market. However, based on all available data, Espicom conservatively estimates that in 2009, the advanced wound care market was worth US$5.1 billion.
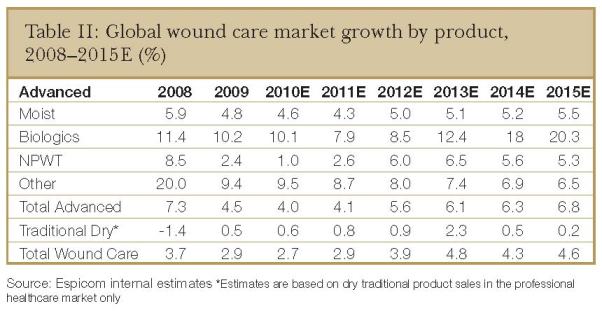
Although the advanced wound care market saw double-digit growth before 2008, the growth rate has slowed more recently. The number of patients requiring treatments for chronic and challenging wounds has and will continue to rise. However, growth in terms of sales volumes is being affected by increasing competition that is bringing down selling prices. In addition, the market is seeing declines in reimbursement levels as governments seek to reign in healthcare expenditure.
Given the fact that pricing is likely to remain weak at least in the short term, but some growth will come from the increasing numbers of chronic wounds and the introduction of new products, Espicom is predicting market growth of approximately 4% for 2011.
5. Opportunities
Each sector of the advanced wound care has its own opportunities and challenges and these are discussed in detail in the Espicom report.
MOIST WOUND DRESSINGS. In brief, this sector of the market is a relatively mature area and many of the market-leading products have been offered for some years, leading to strong brand recognition and user-friendliness. Espicom believes this sector will be negatively affected by weaker pricing and the increased adoption of alternative new technologies. However, some growth will come from the growing use of antimicrobial dressings and the development of new composite products that offer advancements over earlier products.
New products and the increasing interest in technologies that do not lead to antibiotic resistance are expected to lead to market growth in this area. However, there remains little clinical evidence to show the effectiveness of these technologies.
Currently, the most commonly used antimicrobial dressings contain silver, but recent studies of silver-containing products have failed to find a benefit for them compared with products that do not contain silver. So far, demand for silver-containing products has continued to grow. This is despite the negative media attention resulting from the publication of these studies, which indicates the strong market need for antimicrobial dressings. However, growth has slowed somewhat and the products are increasingly being used for infected wounds, rather than to prevent infection from occurring.
Given the high price of silver-containing products, well-designed studies that provide evidence that the products are effective are required for the market to continue to grow. There is also scope for other antimicrobial technologies to take the place of silver products should they be shown to be more clinically effective.
NEGATIVE PRESSURE WOUND THERAPY. In this sector, given the fact that KCI has more than 90% market share, the company's successes and failures drive market growth or declines. Growth is currently being driven by the rising adoption of the technology as awareness increases and more clinical evidence as to its benefits is published. In addition, new applications such as in surgery are expanding the market for NPWT. With approximately 70% of the current market being in the US, there is wide scope to increase adoption in other regions of world.
BIOLOGICAL PRODUCTS. This sector is characterised by more innovation than any other sector of the advanced wound care market, although this is the smallest sector and barriers to market entry are the highest. Although Espicom predicts solid market growth for biologic products to 2015, this will be dependant on companies having the funds to bring products to market and successfully completing their clinical development programmes. These products can also often mean a change of practice for users and a higher cost than older products, which may affect adoption rates and therefore the development of this market.
Espicom's report, "The Global Advanced Wound Care Market to 2015," includes competitive evaluations of major and emerging companies, regional perspectives and insights into opportunity areas.
Reference:
http://www.med-techinnovation.com/Articles/articles/article/15
Copyright © 4L Health Co., Ltd. & Foryou Medical Electronics Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.